While both blogs and websites are online spaces, a blog is a type of website focused on regularly updated content and often used for sharing opinions and information, while a website is a broader collection of web pages with a more static and structured format.
Guiding Questions
- How does the author use language to engage and persuade the audience in the digital format?
- In what ways does the visual design of the webpage enhance or detract from the message?
- How do embedded images, videos, or hyperlinks contribute to the argument or overall purpose of the blog?
- How is the content structured to suit online readers?
- How does the interplay between text and multimedia elements create a cohesive argument?
- What techniques are used to keep the audience’s attention in a digital setting?
- How does the blog or webpage address its target audience’s needs or expectations?
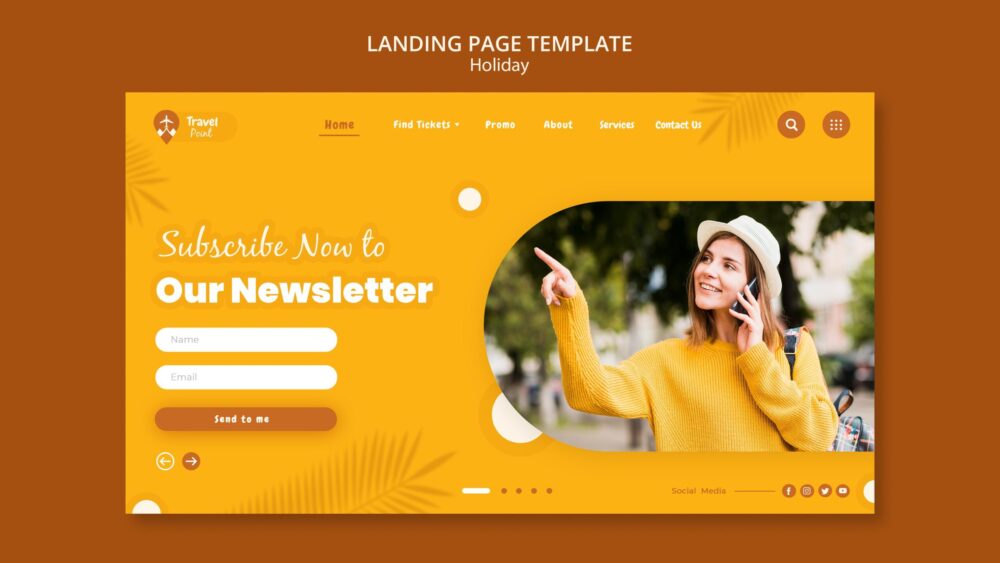
Elements of a Website
Here is a detailed list of elements to be analyzed on a web page and blog. Although the two are not the same, most elements share space.
- Text: Provides the main content, including information, arguments, or storytelling. It’s the core medium for communication.
- Headings: Organizes content into sections and makes it easier to scan. They guide readers through the post’s structure.
- Subheadings: Break down sections into smaller parts, improving readability and providing more detailed guidance.
- Images: Visual elements that support or enhance the content. They make the blog more engaging and visually appealing.
- Videos: Embedded video content adds depth or an alternative format for conveying complex topics or showcasing demonstrations.
- Audios: Podcasts or audio clips cater to readers who prefer listening over reading, adding versatility to the blog.
- Links (Hyperlinks): Connect readers to related resources, enhancing their knowledge or providing references.
- Contact Information: Allows readers to connect with the blog author, contributing to engagement and networking.
- Header: Found at the top of the page, typically includes the blog’s title, logo, and menu navigation. It’s the first thing readers see.
- Footer: Appears at the bottom of the page, often containing copyright information, privacy policies, and additional links.
- Sidebars: Provide extra features, such as recent posts, social media links, or subscription options, without interfering with the main content.
- Navigation Menu: Helps users move seamlessly through the blog by providing links to different categories, pages, or sections.
- Tags/Keywords: Allow better organization of the blog’s content and improve search engine optimization (SEO).
- Categories: Group posts into topics or themes, making it easier for readers to find related content.
- Call-to-Actions (CTAs): Encourages readers to take specific actions, like subscribing, commenting, or sharing.
- Author Bio: A brief section introducing the blog’s author, building trust and personal connection with readers.
- Comment Section: Facilitates interaction between the blogger and readers, allowing feedback and discussions.
- Social Sharing Buttons: Makes it easy for readers to share blog posts on social media platforms, increasing visibility.
- Email Subscription Box: Allows readers to subscribe to the blog for updates, building a loyal audience.
- Search Bar: Enables readers to search for specific content within the blog, improving accessibility.
- Quotes: Highlight impactful or important statements, drawing attention to key points in the content.
- Graphs/Charts: Visual data representations that provide clarity for numbers or trends discussed in the content.
- Bullet Points/Lists: Simplify complex information into digestible parts, improving readability.
- Advertisement Spaces: Generate revenue or promote relevant products and services alongside the content.
- About Page Link: Provides detailed information about the blog’s purpose, goals, or backstory, adding credibility.